Working with Excel files in .NET: OpenXML vs EPPlus vs ClosedXML
If you have ever had to generate Excel reports in C#-based applications, you know the pain of choosing from too many libraries with too many tradeoffs. Some are extremely powerful but painful to write, while others are friendly but struggle with large files. You probably come across OpenXML, EPPlus, and ClosedXML as the top choices among C# developers for Excel integration in .NET applications. In this post, I will outline the benefits and drawbacks of each and demonstrate, with code, how they differ when implemented.
OpenXMLSDK
OpenXML SDK is a library developed by Microsoft to work with Office documents like Word, Excel, and PowerPoint. OpenXML is an open-source framework that allows the manipulation of documents adhering to the Office Open XML File Formats specification.
Basic Excel manipulation with OpenXMLSDk
To use OpenXMLSDK in a C# application, follow these steps.
Step 1: Create a console project
To keep implementation straightforward, I will use a console app. Run the command to create a console project.
dotnet new console -n ExcelComparisonDemo
cd ExcelComparisonDemoStep 2: Install the package
Install the DocumentFormat.OpenXml NuGet package.
dotnet add package DocumentFormat.OpenXmlStep 3: Implement OpenXML for creating an Excel file with data
using DocumentFormat.OpenXml;
using DocumentFormat.OpenXml.Packaging;
using DocumentFormat.OpenXml.Spreadsheet;
static void GenerateWithOpenXml(string filePath)
{
using var spreadsheet = SpreadsheetDocument.Create(filePath, SpreadsheetDocumentType.Workbook);
var workbookPart = spreadsheet.AddWorkbookPart();
workbookPart.Workbook = new Workbook();
var worksheetPart = workbookPart.AddNewPart<WorksheetPart>();
var sheetData = new SheetData();
worksheetPart.Worksheet = new Worksheet(sheetData);
var sheets = spreadsheet.WorkbookPart!.Workbook.AppendChild(new Sheets());
sheets.Append(new Sheet { Id = spreadsheet.WorkbookPart.GetIdOfPart(worksheetPart), SheetId = 1, Name = "Report" });
// Header Row
var headerRow = new Row();
headerRow.Append(
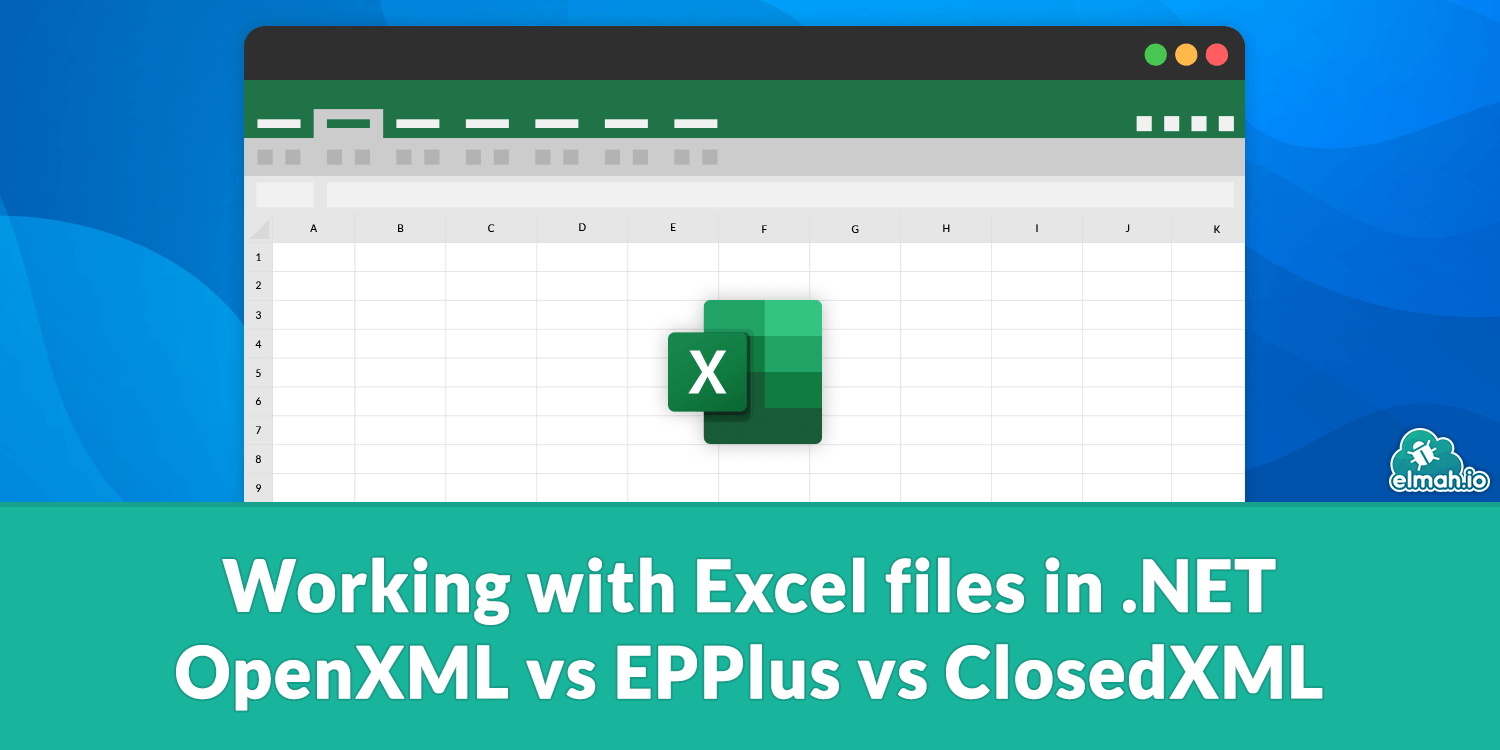
new Cell { CellValue = new CellValue("Product"), DataType = CellValues.String },
new Cell { CellValue = new CellValue("Quantity"), DataType = CellValues.String },
new Cell { CellValue = new CellValue("Price"), DataType = CellValues.String }
);
sheetData.Append(headerRow);
// Data Rows
string[,] data = { { "Apple", "10", "1.20" }, { "Banana", "20", "0.80" }, { "Orange", "15", "1.00" } };
for (int i = 0; i < data.GetLength(0); i++)
{
var row = new Row();
for (int j = 0; j < data.GetLength(1); j++)
{
row.Append(new Cell { CellValue = new CellValue(data[i, j]), DataType = CellValues.String });
}
sheetData.Append(row);
}
workbookPart.Workbook.Save();
}
SpreadsheetDocument.Create creates a new Excel file at the specified location. Every Excel file contains a workbook part that is similar to a table of contents, which references the worksheets within the file. The statement workbookPart.Workbook = new Workbook(); attaches a blank workbook to this part, creating the container that will hold all the sheets.
A Workbook is the top-level container that holds all worksheets. A worksheet represents a single tab or sheet inside an Excel file. Using AddNewPart<WorksheetPart>(), a new sheet part is generated. In contrast, with AppendChild(new Sheets()), I created a sheet file and added it to the Workbook.
Sheet data contains a data grid with rows and columns, represented by the sheetData object. With the code worksheetPart.Worksheet = new Worksheet(sheetData);, it is added to the worksheet. Next, I added the Header row with its cells in the sheetData grid. Finally, I added data rows and saved the Workbook. Each step performs low-level interaction with the XML.
Step 4: Call the method in Program.cs
GenerateWithOpenXml(Path.Combine(basePath, "OpenXmlReport.xlsx"));Step 5: Run the project
dotnet runAfter running, the desired Excel file is created
Benefits of OpenXML SDK
- Does not require any additional helper libraries or COM.
- Good at manipulating the raw XML in a natural Excel manner.
- Works best if a template is predefined. Offers memory-efficient operations, making it suitable for large datasets.
- Enables users to have granular control over styles, shared strings, and formulas.
Downsides of OpenXML SDK
- Has a verbose code that is difficult for early deployments.
- Required time to add checks dealing with accidentally generating invalid data.
- Need to define formatting to eliminate parsing and formatting issues. Shifting rows and columns is problematic with OpenXML.
- OpenXML has a steep learning curve and requires XML format information to work with.
- You must manually construct cell formats, which can be tedious for creating styled reports. Its verbose nature decimates maintainability.
- To evaluate Excel formulas in .NET, users can write them, but Excel executes those formulas.
EPPlus
Developed by EPPlus Software, EPPlus is a .NET Framework spreadsheet library that enables manipulation of Office Open XML files. It offers high-level methods that ease developers' work with Excel.
Basic Excel manipulation with EPPlus
EPPlus is a licensed library and does not offer any free version for commercial use. We will review its coding implementation to understand how to accomplish the prior example of Excel creation in EPPlus.
As we are using the same project, we will continue from step 2.
Step 2: Install the EPPlus NuGet package
dotnet add package EPPlusStep 3: Define a method for creating the Excel with EPPlus
using OfficeOpenXml;
static void GenerateWithEPPlus(string filePath)
{
ExcelPackage.LicenseContext = LicenseContext.NonCommercial;
using var package = new ExcelPackage();
var ws = package.Workbook.Worksheets.Add("Report");
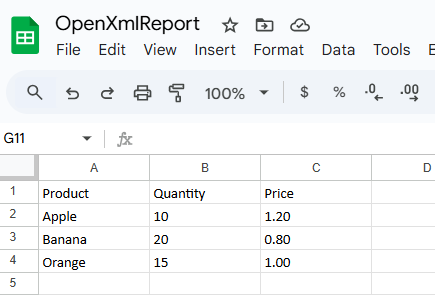
ws.Cells["A1"].Value = "Sales Report";
ws.Cells["A1"].Style.Font.Bold = true;
// Header
ws.Cells["A3"].LoadFromArrays(new object[][] {
new object[] { "Product", "Quantity", "Price" }
});
ws.Cells["A3:C3"].Style.Font.Bold = true;
// Data
var data = new[]
{
new object[] { "Apple", 10, 1.20 },
new object[] { "Banana", 20, 0.80 },
new object[] { "Orange", 15, 1.00 }
};
ws.Cells["A4"].LoadFromArrays(data);
ws.Cells.AutoFitColumns();
package.SaveAs(new FileInfo(filePath));
}
The ExcelPackage.LicenseContext = LicenseContext.NonCommercial line specifies a license using ExcelPackage. Next, the initialization of a new ExcelPackage creates a new workbook. ExcelPackage is more than a workbook; it includes a complete Excel package with workbook metadata, worksheets, styles, formulas, charts, etc.
Then I added a worksheet named "Report" by adding it to the Workbook property's Worksheets collection. Other snippets are self-explanatory as they don't manipulate XML at the low level. First, I set a heading cell and made its text bold with:
ws.Cells["A1"].Value = "Sales Report";
ws.Cells["A1"].Style.Font.Bold = true;
Later, in the part, you can notice a high-level method LoadFromArrays that sets headers from an array. Applying any format is as easy as setting C# properties, as seen in the next line. Finally, data is populated, column auto-fit is used, and everything is saved.
Step 4: Use the GenerateWithEPPlus method in the Program.cs
GenerateWithEPPlus(Path.Combine(basePath, "EPPlusReport.xlsx"));Step 5: Run the project and test
dotnet run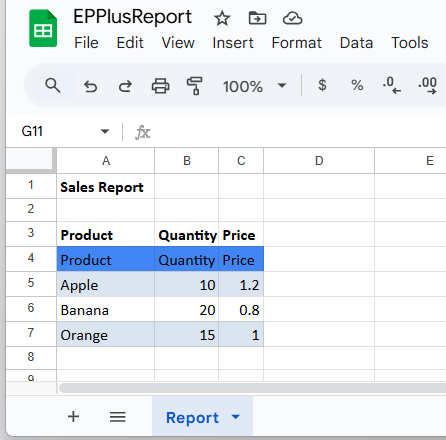
Benefits of EPPlus
- Offers a wide range of Excel features, including charts, formulas, pivot tables, data validation, and conditional formatting.
- EPPlus is a growing community and offers charting. Includes high-level methods for object-to-Excel mapping, such as
LoadFromCollection()andLoadFromArrays(). - Supports encryption and a password to protect read/write access to sheets.
- Enable setting workbook passwords.
- Backed by a big community and standard support.
Downsides of EPPlus
- Does not offer a free version for commercial use, which can be limiting for smaller companies or open-source developers.
- Loads all the data into memory when working with a few thousand rows, which can slow down the application for resource-intensive scenarios.
- Does not allow tweaking XML due to high abstraction.
ClosedXML
ClosedXML is a user-friendly open-source .NET library for reading, writing, and manipulating Excel.
Basic Excel manipulation with ClosedXML
Let's see how our final player works. We will continue the same project for the ClosedXML. Starting with Step 2.
Step 2: Install the ClosedXML package
dotnet add package ClosedXMLStep 3: Create an Excel creation method
static void GenerateWithClosedXml(string filePath)
{
using var wb = new XLWorkbook();
var ws = wb.Worksheets.Add("Report");
ws.Cell("A1").Value = "Sales Report";
ws.Cell("A1").Style.Font.Bold = true;
// Header
ws.Cell("A3").Value = "Product";
ws.Cell("B3").Value = "Quantity";
ws.Cell("C3").Value = "Price";
ws.Range("A3:C3").Style.Font.Bold = true;
// Data
var data = new[]
{
new { Product = "Apple", Quantity = 10, Price = 1.20 },
new { Product = "Banana", Quantity = 20, Price = 0.80 },
new { Product = "Orange", Quantity = 15, Price = 1.00 }
};
ws.Cell("A4").InsertTable(data);
ws.Columns().AdjustToContents();
wb.SaveAs(filePath);
}Working with ClosedXML is a breeze. You don't need to set XML at each level. I simply added an XLWorkbook to initialize the workbook. Then the Report sheet is added as if it were a C# collection. I added some styling to the main heading, and added headers one by one with the cell's Value property. Afterwards, a data array containing data rows is added with the InsertTable method. Finally, column widths are auto-adjusted, and the workbook is saved.
Step 4: Call the method
GenerateWithClosedXml(Path.Combine(basePath, "ClosedXmlReport.xlsx"));Step 5: Run and test the results
dotnet run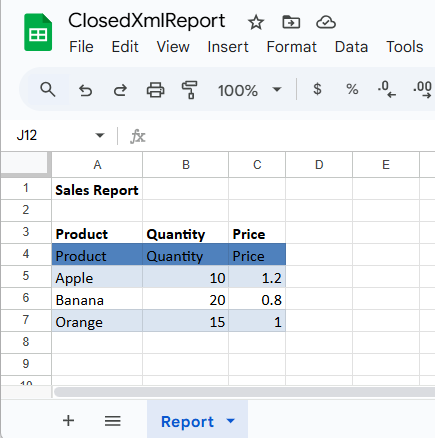
Check out our post Export data to Excel with ASP.NET Core for a longer example of exporting with ClosedXML from an ASP.NET Core application.
Benefits of ClosedXML
- Offers an easy syntax similar to C# objects, such as
ws.Cell("A3").Value = "Product". - Less and handy syntax accelerates development time, making it ideal for quick reports.
- Offer a clean LINQ-friendly API for reading data back into objects.
- ClosedXML is MIT-licensed and is 100% free for commercial and open-source use.
- Backed by an active GitHub community for bug fixing and updates.
- Has a built-in cell format like date and currency.
Downsides of ClosedXML
- Can burden memory for a large data set as it loads the entire workbook into memory.
- ClosedXML is designed for small to medium datasets. Working with more than 100k rows can slow down the application or even crash it.
- Supports primarily the modern Excel version of Office 2007 and later, with the
.xlsxextension. It may not work well with older versions of the software.
Conclusion
Excel is a convenient option for reporting and data insertion for the application. When C# developers face the scenario of integrating Excel into a .NET application, they are overwhelmed by the choices. To solve the problem and clarify tradeoffs, I provided a detailed analysis of the positives and negatives of a few popular spreadsheet libraries, OpenXML, EPPlus, and ClosedXML.
We found that OpenXML is more verbose and requires an understanding of XML and Excel. EPPlus offers its features in the commercial version and is not free, unlike the other two counterparts. ClosedXML is an intuitive tool with high-level methods that are suitable for small to medium-sized applications.
elmah.io: Error logging and Uptime Monitoring for your web apps
This blog post is brought to you by elmah.io. elmah.io is error logging, uptime monitoring, deployment tracking, and service heartbeats for your .NET and JavaScript applications. Stop relying on your users to notify you when something is wrong or dig through hundreds of megabytes of log files spread across servers. With elmah.io, we store all of your log messages, notify you through popular channels like email, Slack, and Microsoft Teams, and help you fix errors fast.
See how we can help you monitor your website for crashes Monitor your website
